
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, School of Physics and Astronomy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
2 Zhejiang Rongjun Hospital, Jiaxing 314000, China
3 School of Pharmacy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
4 Department of Cardiology, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200240, China
5 Collaborative Innovation Centre of Light Manipulations and Applications, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250358, China
Cancer is one of the most common diseases to threaten human health. If individuals are diagnosed with malignant tumors via a single cell, medical workers are greatly advantageous to early diagnose and intervene in malignant tumors therapy. In this paper, we propose a fluorescence detection map to rapidly distinguish whether the chromosomes of a cell are normal or abnormal by detecting the fluorescent intensity of a single cell. Herein, we draw a map from a single cell with an abnormal number of chromosomes that is monitored in real time. Moreover, this way offers precise and prompt detection of the surviving of cancer cells at or near the site of the tumor after treatments for cancer, which can achieve personalized cancer diagnosis and therapy. Therefore, cancer recurrences and metastasis can be effectively identified, utilizing this ultrasensitive detection method of an abnormal chromosome number.
Photonics Research
2021, 9(12): 12002381
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Internet of Things Engineering, Hohai University, Changzhou 213022, China
2 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
3 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
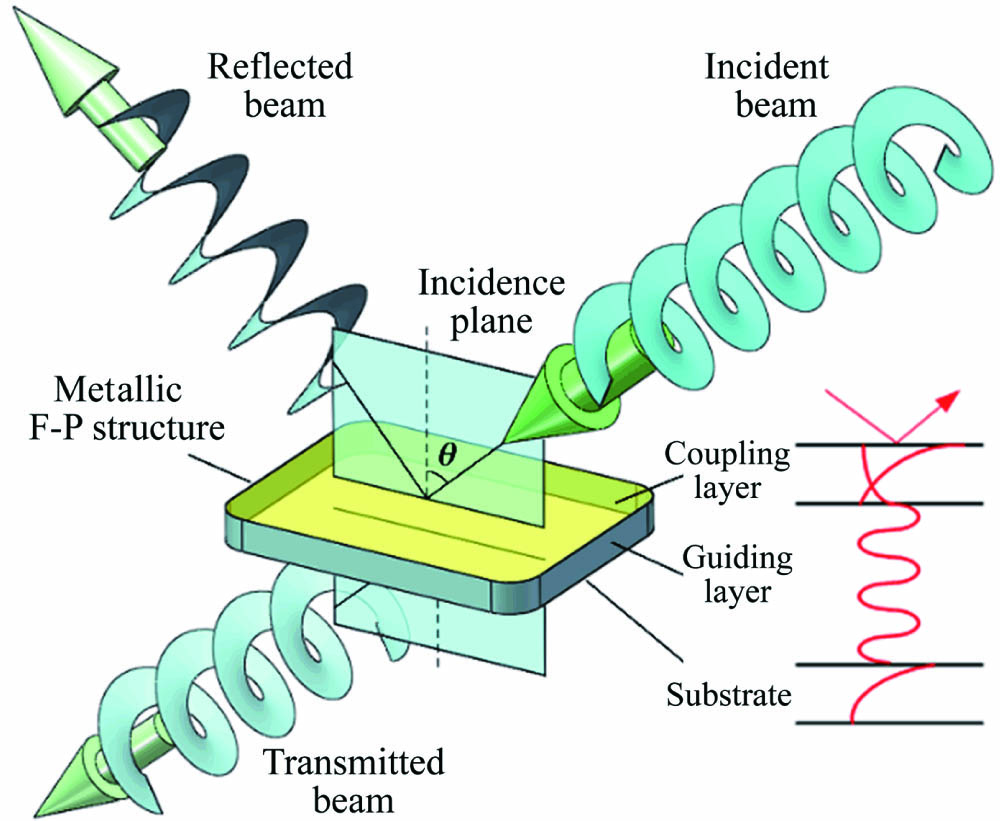
In modern optics, particular interest is devoted to the phase singularities that yield complicated and twisted phase structures by photons carrying optical angular momentum. In this paper, the traditional M-line method is applied to a vortex beam (VB) by a symmetric metal cladding waveguide chip, which can host numerous oscillating guided modes via free space coupling. These ultrahigh-order modes (UOMs) result in high angular resolution due to the high finesse of the resonant chip. Experiments show that the reflected pattern of a VB can be divided into a series of inner and outer rings, whilst both of them are highly distorted by the M-lines due to the UOMs’ leakage. Taking the distribution of the energy flux into account, a simple ray-optics-based model is proposed to simulate the reflected pattern by calculating the local incident angle over the cross section of the beam. The theoretical simulations fit well with the experimental results, and the proposed scheme may enable new applications in imaging and sensing of complicated phase structures.
vortex beam M-line method planar waveguide Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(7): 071403
1 南通大学 理学院,江苏 南通 226019
2 江西师范大学 物理与通信电子学院,江西 南昌 330022
3 上海交通大学 物理系,上海 200240
针对一般光反应器的不足,双面金属包覆波导能够把光耦合进入导波层中激发出超高阶导膜,波导中入射波与反射波相互叠加形成驻波,继而在导波层中出现一系列的光能量增强点(被认为是光陷阱点)。基于这种光学特性,设计了一种新颖的液芯双面金属包覆波导光反应器。采用含有二价铁离子和三价铁离子的混合盐溶液充当导波层,激光耦合进入导波层中两小时后,在该种特定光场分布的作用下,制备出了合成产物。通过对产物的分析,确定合成产物为磁铁矿γ-Fe2O3。
超高阶导膜 驻波 液芯波导光反应器 磁铁矿 ultrahigh order mode standing wave liquid-core waveguide optical reactor magnetite
1 铜仁学院物理与电子科学系, 贵州 铜仁 554300
2 上海交通大学物理系区域光纤通信网和新型光通信系统国家重点实验室, 上海 200240
以亚毫米尺度的铌镁酸铅钛酸铅(PMN-PT)透明陶瓷片为导波层制备了对称金属包覆波导,并利用自由空间耦合技术激发了波导中的超高阶导模。根据衰减全反射(ATR)峰的移动,得到了在波导两侧所施加电压与光强反射率的关系,从而计算了PMN-PT透明陶瓷片的二次电光系数。
光学器件 镁银酸铅钛酸铅 二次电光系数 衰减全反射 灵敏度 光学学报
2011, 31(10): 1012002
1 铜仁学院物理与电子科学系, 贵州 铜仁 554300
2 上海交通大学物理系区域光纤通信网和新型光通信系统国家重点实验室, 上海 200240
3 菲尼萨光电通讯有限公司, 上海 201201
根据对称金属包覆电光波导中本征损耗与古斯亨兴(Goos-Hnchen)位移的理论公式,导出了古斯亨兴位移与作用于波导两侧电压的二次关系公式。用622 μm厚度的四方相铌镁酸铅钛酸铅(PMN-PT)透明电光陶瓷片作为导波层制备了对称金属包覆波导,测量了古斯亨兴位移与作用于波导两侧电压的关系曲线,计算了所用透明电光陶瓷片的二次电光系数。实验结果与理论分析一致。
非线性光学 古斯亨兴位移 光波导 四方相铌镁酸铅钛酸铅
1 江西师范大学 物理与通信电子学院,江西 南昌 330022
2 上海交通大学 导波光子学实验室,上海 200240
利用光频范围贵金属介电常量的虚部远小于其实部绝对值的特点,采用一阶微扰理论得到了对称金属包覆波导横电和横磁导模微扰传播常数的解析公式。针对金属包覆波导传输损耗大的缺陷,提出采用亚毫米尺度的超厚导波层来抑制传输损耗的新方法。微扰公式与精确数值解结果相符。
光学设计 光波导 超高阶导模 微扰理论 传输损耗
1 江西师范大学物理与通信电子学院, 江西 南昌 330022
2 上海交通大学导波光电子器件实验室, 上海 200240
利用自由空间耦合技术,用超短脉冲激发亚毫米尺度对称金属包覆波导中的超高阶导模,提出一种脉冲展宽的新方法。由于超高阶导模的强色散性质,经过短距离的传输,即可使脉冲宽度迅速展宽。理论分析表明,1 ps的光脉冲在光波导中传输毫米量级距离后,脉冲展宽因子可达到1000倍。
激光技术 对称金属包覆介质波导 脉冲展宽 自由空间耦合技术 超高阶导模
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 800 Dong Chuan Road, Shanghai 200240, PR China
2 National Laboratory of High Power Laser and Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 390 Qing He Road, Box 800-211, Shanghai 201800, PR China
We present a nondestructive technique to predict the refractive index profiles of isotropic planar waveguides, on which a thin gold film is deposited to as the cladding. The negative dielectric constant of the metal results in significant differences of effective indices between TE and TM modes. The two polarized modes and a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) with abundant information of the surface index can be used to construct the refractive index profiles of single-mode and two-mode waveguides at a fixed wavelength.
Refractive index profile SPR method Few-mode isotropic waveguides TE and TM modes Collection Of theses on high power laser and plasma physics
2006, 4(1): 150
用棱镜耦合法在质子交换LiNbO3平面光波导两端激发相对传播的光导波,在导波交迭处观察到垂直于波导表面出射的倍频光,实现了非简并四波混频.





